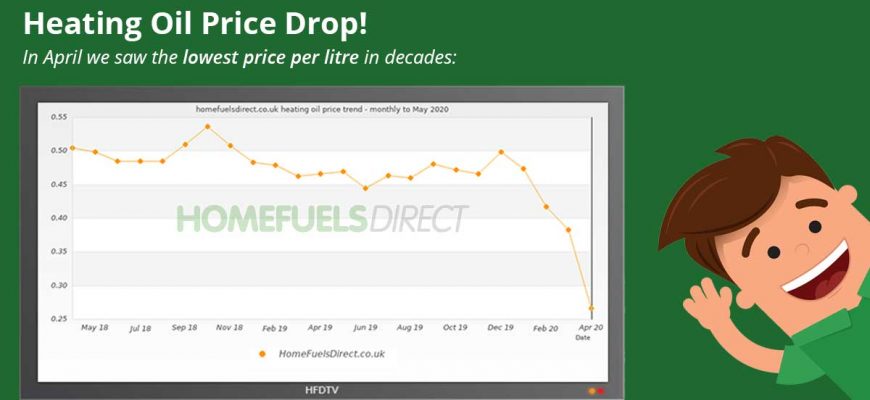
Exploring the Potential Trends in Furnace Oil Prices and Their Possible Decline
The world of energy consumption is a constantly evolving landscape, shaped by a multitude of factors ranging from global demand to geopolitical tensions. As households and industries strive to manage their expenditures, the conversation around these fluctuations becomes ever more relevant. Understanding what influences these shifts can help consumers and businesses alike navigate the complexities of this market.
In recent times, many have found themselves pondering the trajectories of heating materials that play a crucial role in maintaining warmth during colder months. With the ongoing shifts in regulations and economic conditions, shifts in available resources can lead to unpredictable outcomes. It’s easy to feel unsettled when trying to anticipate such transformations.
As we delve deeper into this topic, it’s essential to consider the driving forces behind these changes. By examining supply chains, demand forecasts, and external factors, we can gain insight into whether relief from escalating costs may be on the horizon. Join us as we explore the dynamics at play and what they might mean for consumers in the near future.
The Current Trends in Energy Costs
The world of energy expenditure is always on the move, influenced by a myriad of factors that shape its trajectory. One moment we can witness soaring rates and the next, a shift may lead to more favorable conditions for consumers. Understanding these fluctuations can be vital for both homeowners and businesses alike.
Recent patterns indicate that demand plays a crucial role in determining how much consumers need to fork out. Factors such as economic growth, seasonal changes, and geopolitical dynamics often contribute to these shifts. When demand surges, especially in colder months or during peak usage times, we typically see an uptick in costs, creating a ripple effect throughout various sectors.
On the flip side, technological advancements and alternative energy sources are beginning to reshape the landscape. As more people turn to renewable energy options, traditional sources face mounting pressure to adapt. This can potentially lead to more competitive rates down the line, depending on market responses and consumer choices.
Moreover, global events like natural disasters, political tensions, and regulatory changes can rapidly alter the equilibrium. Monitoring these influences offers insight into potential future developments regarding what one might expect in terms of expenditure.
Ultimately, keeping an eye on these evolving dynamics will help individuals make informed decisions, whether it’s for their homes or businesses. Adapting to the current market can lead to significant savings in the long run.
Factors Influencing Heating Fuel Costs
Understanding what drives the expenses associated with heating fuel can be quite enlightening. Several elements come into play that collectively impact consumer spending and market trends. From global supply chains to local demand fluctuations, each factor adds a layer of complexity to this ever-evolving landscape.
One of the most significant contributors is the cost of crude substances on the international market. Changes in extraction efforts, geopolitical tensions, or natural disasters can all affect these figures. Additionally, the refining process and transportation logistics also play a crucial role. If it becomes more costly to get the final product to your neighborhood, you can expect that expense to trickle down to the consumer.
Another important aspect is seasonal demand. Colder months typically see a spike in consumption as people seek warmth. This increased usage can drive up costs during peak times. Conversely, milder weather can lead to reduced demand and potentially lower expenses.
Regulatory policies are also influential. Government decisions around environmental standards, taxation, and subsidies can shift the economic balance. For instance, stricter regulations might lead to higher operational costs for producers, which could, in turn, impact what consumers pay.
Lastly, market speculation can affect how consumers perceive upcoming expenses. Traders and investors often react to news and forecasts, which can create fluctuations independent of actual supply and demand. Understanding these dynamics helps consumers make informed choices regarding their heating options.
Future Predictions for Energy Costs
As we look ahead, many are curious about how the landscape of energy expenditures will evolve. Various factors come into play, including global events, supply chain dynamics, and changing consumer behaviors. Understanding these elements can help us form an educated guess about the trajectory of energy expenses in the near future.
Market trends suggest that fluctuations in demand could significantly influence overall expenses. For instance, as more individuals embrace sustainable alternatives, traditional energy sources may see a decrease in consumption. This shift could lead to adjustments in costs, as providers react to evolving market conditions.
Additionally, geopolitical factors often create ripples in the energy sector. Conflicts, trade agreements, or regulatory changes can have immediate impacts, affecting the affordability of various energy resources. Therefore, keeping an eye on international relations and policy shifts is crucial for understanding potential changes.
Lastly, technological advancements are paving the way for more efficient energy solutions. As innovation continues to reshape how we produce and utilize energy, we may anticipate a more stable environment that could benefit consumers in the long run. Overall, being informed about these dynamics can help everyone prepare for what lies ahead in the energy market.