The Future of the Eurozone – Which Countries Are Likely to Adopt the Euro Next
As Europe continues to evolve, many nations are contemplating the prospect of unifying under a common currency. This ongoing dialogue raises intriguing questions about potential candidates and the implications of adopting a shared monetary system. The conversation isn’t solely about economic advantages; it also encompasses political, cultural, and social dimensions that can reshape relationships between neighboring states.
Recent developments have sparked renewed interest in this topic, with several countries showcasing their aspirations for deeper integration. The allure of seamless travel, trade benefits, and enhanced stability make this proposition attractive. Yet, challenges persist, including public opinion and the readiness of these nations to meet the required benchmarks for participation.
With an ever-changing landscape, discussions surrounding future entrants into this monetary framework are gaining momentum. Each potential participant brings unique strengths and hurdles, contributing to a dynamic conversation that reflects the complex nature of European unity. As we explore these possibilities, it’s essential to consider the diverse factors at play that can either facilitate or hinder this journey toward economic collaboration.
Potential Candidates for Eurozone Membership
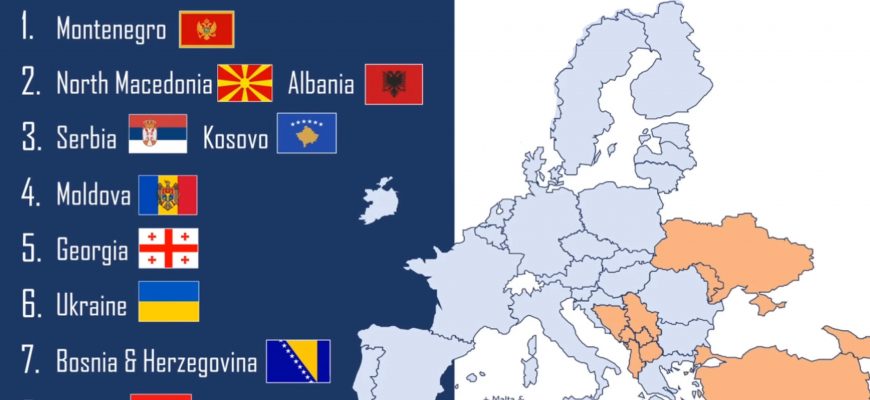
When we think about countries eyeing integration into the currency club, several contenders pop up on the radar. Each nation brings its own unique circumstances and motivations for seeking adoption of a unified monetary framework. Understanding their situations can shed light on what drives their aspirations.
Poland emerges as a prominent player in this discussion. With a robust economy and significant trade ties to the Eurozone, the incentive for transitioning to a common currency is quite strong. However, political dynamics and public sentiment can shape the pace of this shift.
Next on the list is Hungary. The nation has enjoyed consistent economic growth in recent years. Despite some hesitations regarding fiscal policy alignment with European standards, Hungary remains a strong candidate for eventual integration.
Another noteworthy contender is Czech Republic. The country’s stable economy and favorable investment climate make it an attractive prospect. However, like others, there are concerns related to public acceptance and alignment with the European Central Bank’s requirements.
Lastly, we cannot overlook Romania. With improvements in its economic landscape and aspirations for greater inclusion in European frameworks, Romania is working toward aligning with the relevant criteria, although challenges remain on its path.
In summary, while aspirations for adopting a new currency vary from nation to nation, the prospects for these candidates reflect a broader desire for economic stability and integration within Europe. It will be interesting to track how these ambitions evolve over time.
Economic Implications of Currency Embracement
Adopting a new monetary system can significantly reshape a nation’s economic landscape. Transitioning to a shared currency often brings about a blend of opportunities and challenges that can affect trade, investment, and overall economic stability. Understanding these elements is crucial for any country considering such a change.
When a nation shifts to a unified currency, it may experience reduced transaction costs. Businesses no longer face currency exchange fees when trading with partners in member countries, which can stimulate cross-border commerce. Furthermore, price transparency increases as consumers can easily compare prices, potentially fostering competition and optimizing market efficiency.
However, integrating into a broader monetary system also entails certain risks. A country may find itself subjected to fiscal policies set by a central authority, limiting its capacity to respond to local economic conditions. This can lead to complications, especially in times of economic downturns, where individual nations might require tailored monetary strategies that a collective framework cannot provide.
Additionally, the stability of the new currency plays a crucial role. If the collective economy faces crises, the repercussions can spread to member states, affecting employment rates and public services. Therefore, maintaining a balance between local autonomy and the benefits of a centralized currency is essential for long-term success.
In the grand scheme of things, while embracing a new monetary system offers promising advantages, it also requires careful consideration of associated economic dynamics. Countries must navigate the complexities of integration while ensuring that the benefits outweigh potential drawbacks for their citizens.
Challenges Facing New Currency Adopters
Embracing a new monetary system is no small feat, and many nations face a myriad of hurdles in this transformative journey. Transitioning to a shared currency entails not only technical adjustments but also significant economic and political implications. It’s essential to examine the obstacles that lie ahead for countries eager to take this step.
One major challenge is aligning national economic policies with those of the broader community. Ensuring fiscal discipline while accommodating individual economic needs can create tension. Additionally, there’s the task of managing public perception and gaining taxpayer confidence. Citizens may have concerns about the implications of such a switch on their daily lives and financial stability.
Another critical aspect is the potential impact on trade relationships. Establishing competitive trade conditions while adapting to a new marketplace can be daunting. Exporters and importers must adjust to fluctuations in pricing and exchange rate mechanisms, which can create uncertainty.
Finally, technical infrastructure plays a vital role. Countries must invest in modernizing their financial systems to support new payment methods and streamline transactions. This often requires significant investment and careful planning to avoid disruptions during the transition period.
In summary, while the path to adopting a new currency looks promising, the journey is fraught with challenges that need strategic solutions and careful management.