A Comparative Analysis of the Student Aid Index and the Estimated Family Contribution in Financial Planning for Education
Navigating the world of higher education financing can often feel overwhelming. Many individuals and families are confronted with the challenge of deciphering various financial support mechanisms available for pursuing academic goals. Two essential terms frequently pop up in this discussion, and understanding their distinctions is crucial for effective planning.
These financial tools serve as yardsticks to gauge the monetary resources available to potential students. They take into account various elements such as income levels, savings, and overall financial situation. By grasping how each instrument functions, people can make informed decisions about funding their educational journeys and maximizing available resources.
In this article, we will explore the differences between these two pivotal financial metrics, shedding light on how they impact the journey toward securing the support necessary for academic success. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to tackle your educational aspirations.
Understanding the Financial Support Metric
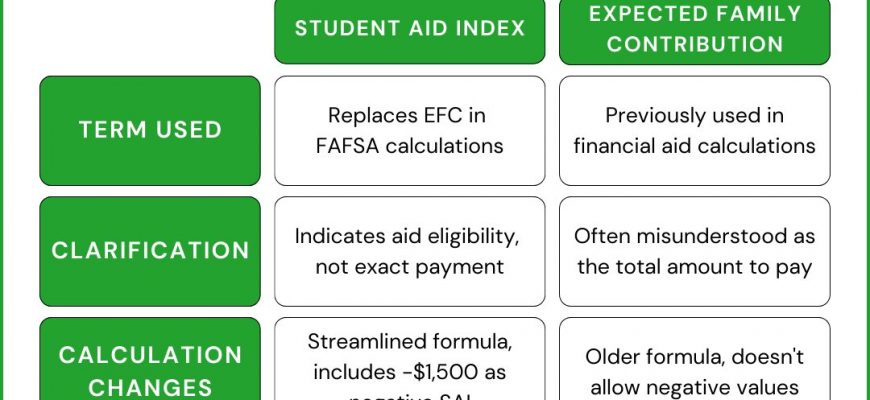
When it comes to funding education, many factors come into play, all aimed at assessing how much families can contribute toward tuition and expenses. This particular measure plays a critical role in determining the level of financial assistance a student may qualify for. It’s essential to grasp how this measurement works and what it indicates about a family’s financial standing.
This metric considers various aspects of a household’s financial health, including income, assets, and other relevant data. By evaluating these components, authorities can arrive at a figure that reflects a family’s capacity to support educational costs. This calculation is not just a number; it influences the types and amounts of support available to students, shaping their academic journey.
Understanding this metric also helps families plan better for the future. Parents and guardians can gain insights into how their financial situation might impact their children’s access to educational resources. Awareness of how this figure is determined can empower families to make informed decisions, from saving strategies to determining eligibility for various programs.
Ultimately, grasping this concept allows individuals to navigate the complex world of educational financing with greater ease. Whether you’re a future scholar or a concerned parent, knowing what this figure represents can demystify the process and facilitate a smoother transition into higher learning.
Comparing EFC and Financial Need
When looking at how resources are calculated for higher education, it’s important to understand the difference between overall capacity to contribute and the actual financial requirements. These two concepts play a crucial role in determining how much support someone might receive when pursuing academic goals.
Overall Contribution Capacity reflects the amount a household could potentially spare for education expenses based on various financial indicators. This figure often takes into account factors like income, assets, and other economic elements. On the other hand, Financial Requirement represents the gap between the total cost of attendance and this capacity. It’s the amount that truly indicates the level of support needed to make education accessible.
In essence, while the overall contribution capacity serves as a guideline for what families might afford, the financial requirement gives a clearer picture of actual needs. Understanding both can help individuals navigate funding opportunities more effectively and ensure that they receive the necessary backing to pursue their ambitions.
Implications for College Funding Strategies
When planning for higher education funding, understanding the tools and calculations involved can significantly transform financial approaches. With recent changes in how institutions assess financial support, families need to adapt their methods in order to align their resources effectively.
These alterations may prompt a shift in how individuals view their financial situations and the resources available to them. By grasping the nuances of funding calculations, families can better position themselves to navigate the complexities of tuition costs and available resources. This understanding could lead to more strategic decisions regarding savings, income allocation, and investment in educational resources.
It’s essential to reevaluate financial plans regularly. This allows families to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information about costs and funding opportunities. Engaging with financial consultants or participating in workshops can also provide valuable insights into maximizing benefits from various programs and scholarships.
Ultimately, being proactive rather than reactive can make a significant difference in the overall financial experience of pursuing higher education. A solid grasp of funding evaluations empowers families to explore all options, ensuring that educational aspirations remain attainable without disproportionate financial strain.