A Comparative Analysis of Quantitative Finance and Statistics in Modern Financial Practices
In the world of numbers and data, there exists a fascinating interplay between two fields that often captivate the minds of analysts and researchers alike. These realms, while closely related, offer distinct perspectives on how we interpret information, make predictions, and drive decisions. Navigating through these domains can be both enlightening and challenging, unveiling the power of numerical reasoning in understanding complex systems.
One area focuses on the application of rigorous mathematical techniques to unravel the mysteries of market behavior, leveraging models to forecast potential outcomes and manage risks. The other emphasizes the examination of data trends and patterns, allowing for insightful conclusions based on historical evidence. Together, they paint a comprehensive picture of how we approach challenges in economic environments.
As we delve deeper into these two spheres, it becomes clear that each possesses unique methodologies and tools, yet they often converge in their ultimate goal: to enhance our decision-making processes through a better understanding of numerical information. Whether interested in creating predictive models or drawing insights from past performance, appreciating their differences and overlaps can illuminate pathways to success in various analytical endeavors.
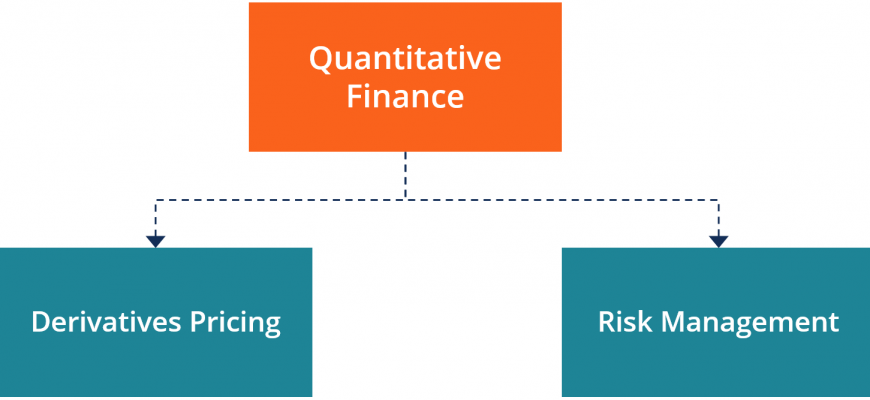
Understanding Mathematical Principles in Market Analysis
In the world of financial markets, a deep dive into numerical methodologies reveals a fascinating interplay between theory and practice. The essence here lies in leveraging mathematical tools to decipher patterns, optimize investment strategies, and manage risks. This blend of analytical reasoning and practical application creates a dynamic framework that informs decision-making processes.
At the core of this discipline is a structured approach to analyzing vast data sets. By employing advanced algorithms and modeling techniques, practitioners can uncover hidden relationships and forecast trends with greater accuracy. The ability to interpret historical data and make informed predictions becomes pivotal, guiding actions in a highly volatile environment.
Another key component involves risk management, where quantitative measures help assess and mitigate potential losses. Understanding different types of risk and utilizing mathematical models enables professionals to devise strategies that not only protect capital but also enhance returns. This critical balance transforms uncertainty into opportunity, making for a compelling aspect of market engagement.
As practitioners delve deeper into this realm, the integration of technology becomes essential. Automated systems and computational tools only enhance the effectiveness of the analytical processes. The marriage of sophisticated software solutions with mathematical frameworks ensures that market players can respond swiftly to changes, seizing advantageous moments as they arise.
Ultimately, mastering these mathematical concepts empowers individuals and institutions alike, providing them with the means to navigate the complexities of financial landscapes confidently. Understanding these principles is not just about crunching numbers; it’s about crafting a narrative that guides actions and fosters informed decision-making underpinned by empirical evidence.
The Role of Statistics in Financial Analysis
When it comes to making sense of numbers in the world of money matters, there’s a powerful tool that helps analysts dig deeper into data. This vital aspect aids in understanding trends, making predictions, and ultimately guiding critical decisions. It brings clarity to the complexities of economic activities and drives insightful conclusions.
At its core, this discipline provides techniques for collecting, reviewing, and interpreting numerical information. Analysts rely on this knowledge to identify patterns and correlations that might not be immediately visible. This can lead to more informed choices about investments, risk assessment, and overall strategy development.
Moreover, having a strong grasp of this domain allows experts to quantify uncertainty and evaluate potential outcomes. By applying models and calculations, they can simulate various scenarios to assess how different factors might influence financial performance. This kind of analysis can significantly enhance strategic planning and risk management approaches.
Using these methods, individuals and organizations can benchmark performance against peers or historical data. This practice not only highlights strengths and weaknesses but can also reveal opportunities for growth and improvement. Ultimately, understanding the nuances within numerical data empowers stakeholders to navigate the often turbulent waters of economic decision-making.
Differences in Methodologies and Applications
When we dive into the world of numbers, it’s fascinating to see how different approaches shape the way we interpret and utilize data. These two fields, while sharing a common ground in dealing with numerical information, diverge significantly in their methods and the contexts in which they thrive. Each discipline has its unique tools and frameworks that cater to specific needs and outcomes, leading to varied applications in real-world scenarios.
One of the main distinctions lies in the techniques employed. One area often relies on complex modeling and sophisticated algorithms to forecast trends and make informed predictions, while the other tends to focus on understanding patterns through descriptive methods and inferential reasoning. This difference in approach not only affects how practitioners analyze data but also influences the eventual conclusions and decisions derived from that analysis.
Moreover, the practical implications of these methodologies widely vary. One domain may prioritize risk assessment and portfolio optimization, essentially enhancing decision-making in financial environments. In contrast, the other might emphasize research and experimentation, using data to draw conclusions and validate hypotheses across diverse fields like healthcare and social sciences. This versatility enables practitioners to tailor their analyses to specific objectives, providing valuable insights tailored to their respective contexts.
Ultimately, the divergence in methodologies and applications highlights the rich tapestry of numerical disciplines. By understanding these differences, we can better appreciate the strengths and limitations of each approach, allowing us to leverage them effectively in various projects and inquiries.