Exploring the Nature and Significance of Credit as a Form of Money
When we think about the means of exchange that drive our economy, it’s easy to get lost in the complexities of terminology. Most people probably see a simple transaction as just that–a straightforward deal. Yet, there is a fascinating world behind that simplicity, one where the concept of what constitutes a valid form of transaction is intriguingly fluid.
Throughout history, this form of exchange has evolved significantly, adapting to the changing needs and technologies of society. What was once tangible and straightforward has morphed into something far more abstract and multifaceted. As we dig deeper, we realize that the essence of this medium goes beyond mere physicality or the common understanding we’ve held. It plays a pivotal role in shaping economic landscapes and influencing daily life.
In this exploration, we will peel back the layers and examine whether what we often take for granted is indeed an intrinsic part of our financial system. Could it be that the framework we rely on to navigate our financial interactions is built on principles that extend far beyond simple transactions? Join us as we navigate these intriguing aspects and delve into the implications and realities of current financial paradigms.
Understanding the Nature of Credit
In today’s world, the concept of borrowing and lending plays a crucial role in facilitating transactions and driving economic growth. It enables individuals and businesses to access resources without needing immediate funds. This system thrives on trust, creating a web of relationships where obligations and promises form the backbone of financial interactions.
At its core, this phenomenon revolves around the idea of exchanging value. When you borrow from a lender, there’s an expectation of future repayment. This relationship shapes how we perceive worth and encourages both personal and communal financial engagement. It’s fascinating to witness how this trust translates into spending power, enriching lives and stimulating commerce.
The mechanics behind this system can be intricate. Various institutions and platforms participate, setting the stage for an array of offerings tailored to different needs. From personal loans to business financing, the options available highlight the flexibility of this approach. Individuals can leverage available tools to make significant purchases or invest in opportunities that might otherwise be out of reach.
Moreover, the impact of this arrangement stretches beyond mere transactions. It influences economic health on a larger scale, dictating trends and shaping policies. Understanding how this ecosystem operates encourages a more informed perspective on one’s own financial decisions, fostering better management and planning for the future.
The Role of Credit in the Economy
In today’s world, the lifeblood of economic growth and development is often found in the ability to borrow. This practice allows individuals and businesses to access necessary resources that they may not currently possess. By leveraging future earning potential, people can invest in opportunities that lead to job creation, innovation, and improved living standards.
Access to loans enables consumers to make significant purchases, such as homes and vehicles, which boosts demand in various industries. This, in turn, creates a ripple effect, stimulating production and leading to job openings. For enterprises, borrowing facilitates expansion efforts, allowing them to increase production capacity or invest in new technologies, driving overall competitiveness.
Furthermore, the dynamic of borrowing and lending cultivates financial systems where trust plays a crucial role. Institutions assess risk and price services accordingly, promoting responsible usage and encouraging individuals to manage their resources effectively. This symbiotic relationship fosters stability and promotes economic resilience, making it essential for navigating challenges.
Ultimately, the interplay between borrowed resources and economic activities underpins much of our financial landscape. It shapes consumer behavior, business strategies, and even influences government policies aimed at fostering growth and stability. The importance of this mechanism cannot be overstated, as it continues to be a driving force behind progress and prosperity.
Differences Between Credit and Cash Systems
When we dive into the financial world, we often encounter two distinct systems that govern how we exchange value. Each has its own set of characteristics, benefits, and limitations. Understanding these differences can help individuals and businesses navigate their financial choices more effectively.
First off, let’s talk about the immediate nature of traditional currency. In this system, transactions are completed right away. When you make a purchase, the specified amount is physically transferred from your possession to the seller’s. It’s straightforward and tangible, allowing for a clear sense of ownership. You can literally hold it in your hands!
On the other hand, when utilizing an alternative mechanism for transactions, the process can be more abstract. Here, the focus shifts towards promises and agreements rather than direct exchanges. You may find yourself making purchases with the understanding that you’ll settle the amount later. This setup often comes with various terms and conditions, such as interest rates and repayment schedules, which can complicate the simple act of buying something.
Moreover, liquidity is another major difference. Traditional currency usually provides immediate liquidity, allowing consumers to have instant access to their funds. Conversely, agreements or obligations may not offer that same level of accessibility, and customers might need to wait before they can actually use what they’ve accumulated.
Finally, the economic implications also differ significantly. In the realm of standard currency, each transaction impacts personal finances directly, promoting mindful spending. In contrast, the alternative system can encourage a more extensive engagement with finance, creating opportunities for accumulating assets but also increasing the risk of overspending if not managed wisely.
In summary, both systems have their unique attributes that cater to different needs and preferences. By recognizing the distinctions, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.





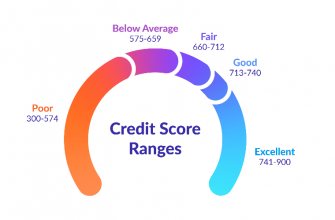


This video is a visual feast. The beauty is simply stunning.