Understanding the Required Number of Credits for Eligibility in Financial Aid Programs
Access to higher learning opportunities often hinges on the support available to students seeking financial resources. Knowing what is necessary to qualify for these benefits can be a daunting task. It’s essential to navigate the various criteria that institutions establish to determine eligibility for assistance.
One of the pivotal factors that come into play in this process has to do with the coursework undertaken by students. The volume of classes and, consequently, the workload one commits to can significantly influence the availability of support. This aspect is crucial for anyone considering additional financial support while pursuing their academic goals.
Exploring this subject further reveals the intricate relationship between academic engagement and the resources available. Understanding the minimum requirements set forth by institutions will empower prospective students to make informed decisions about their educational journey. After all, making the most of available support can pave the way for a successful experience in academia.
Understanding Credit Requirements for Aid
When it comes to securing support for your education journey, there’s an important aspect that often comes into play. This relates to the number of academic achievements one must fulfill to be eligible for assistance. Grasping this concept is crucial, as it directly influences your ability to receive necessary resources while pursuing your studies.
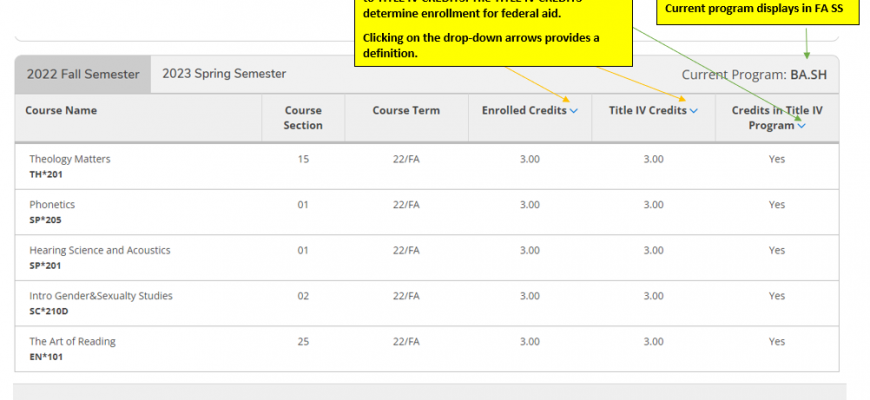
Institutions typically have specific stipulations in place regarding the amount of coursework completed or in progress that qualifies students for various types of support. It’s essential to be aware of these guidelines, as they can vary widely depending on programs, schools, and even types of assistance available. Understanding these parameters can help you navigate your educational path with greater confidence and clarity.
Additionally, the distinction between part-time and full-time enrollment plays a significant role. Often, full-time status is a prerequisite for certain forms of support, while part-time students might find fewer options available. Therefore, it’s advisable to consult your institution’s resources or financial support office to clarify your situation and ensure you’re on the right track.
Evaluating Your Academic Progress
Assessing your educational journey is crucial for making informed decisions about your future. Understanding where you stand academically can open doors to various resources that support your ambitions. It’s not just about hitting benchmarks; it’s about developing a deeper connection to your studies and aligning them with your goals.
To effectively gauge your achievements, consider the following steps:
- Review your transcripts regularly to track your academic performance over time.
- Set personal milestones to maintain motivation and clarity in your objectives.
- Speak with academic advisors who can provide insights tailored to your situation.
It is also valuable to engage with your peers in discussions about progress. Collaboration can enhance understanding and provide additional perspective on various subjects.
Ultimately, remaining proactive in evaluating your accomplishments not only prepares you for upcoming challenges but also maximizes opportunities for support that may be available to you.
Types of Assistance and Requirements
When pursuing higher education, understanding the available forms of support can be crucial. Various options exist to help ease the financial burden, with each having its own set of criteria and stipulations. It’s important to grasp these distinctions, as it can significantly affect your path to obtaining a degree.
Grants are typically need-based and do not require repayment. They are often awarded to students from lower-income backgrounds, making higher education more accessible. On the other hand, scholarships may be merit-based, recognizing achievements in academics, sports, or the arts. These funds also do not require reimbursement, allowing students to focus on their studies without the added stress of debt.
Additionally, work-study programs provide part-time job opportunities, enabling students to earn money while studying. This can be an excellent way to gain experience alongside a paycheck. Lastly, loans present another option, usually requiring repayment after graduation, often at a lower interest rate than other types of borrowing.
To qualify for these resources, students often must maintain a certain level of academic performance or enrollment status. Thus, awareness of these requirements is essential for taking full advantage of the support available.