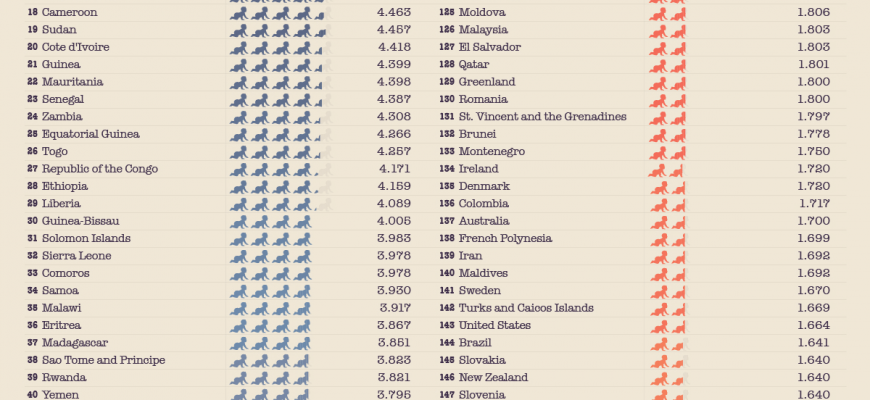
Exploring the Number of Countries That Implement Child Limitation Policies
In various parts of the world, certain strategies have been implemented to manage growth rates and ensure sustainable development. These approaches can range from incentives for smaller families to legal restrictions on reproduction. Such measures often spark a significant amount of debate, as they touch upon personal freedoms, economic implications, and cultural values.
Across different nations, the regulations and guidelines set forth reveal diverse philosophies regarding family size and societal needs. While some governments actively encourage larger households to bolster their workforce, others impose restrictions in hopes of easing resource strain and enhancing quality of life. The effectiveness and ethical considerations of these policies are constantly under scrutiny.
As we delve deeper, it’s crucial to examine the specific legislations and their impacts. The uniqueness of each country’s approach sheds light on broader themes of governance, societal values, and human rights, providing a comprehensive understanding of this intriguing topic.
Understanding Child Limits Worldwide
Numerous nations adopt specific regulations regarding the number of offspring families can welcome. This practice stems from various social, economic, and environmental factors that governments consider essential for their citizens’ well-being. The objective is often to ensure sustainable growth while addressing pressing concerns like resource availability and population dynamics.
Policies relating to offspring can vary significantly from one region to another. Some places implement strict rules, while others merely encourage families to think about the broader implications of their decisions. It’s fascinating to see how different cultures approach the subject, reflecting their unique histories and values.
For instance, in certain areas, governments may offer incentives or penalties based on the number of young ones a family chooses to raise. These measures often spark debates about personal freedom, societal responsibilities, and the role of policy in private life. Discussions surrounding such regulations can reveal a lot about the prevailing attitudes toward family, resources, and future planning.
Population Control Policies Around the Globe
There are certain nations that implement strategies to manage the growth of their citizens. These approaches are often designed to address various issues, such as economic stability, resource management, or environmental sustainability. Though the specifics can differ greatly from one place to another, the overarching goal remains the same: to create a balance between population size and available resources.
In some regions, restrictions and incentives are put in place to encourage smaller family units. This can involve a range of measures, from financial advantages for smaller families to educational campaigns aimed at raising awareness about reproduction. Such policies can stir up debates over individual freedoms versus collective good, reflecting deeply rooted cultural values and social norms.
Interestingly, while some areas exert strict controls, others may offer more flexible guidelines, allowing families to choose. Each nation’s approach is influenced by its unique socio-economic situation, historical context, and demographic challenges, creating a fascinating tapestry of population management strategies worldwide.
Impact of Restrictions on Offspring
The phenomenon of regulating the number of offspring can lead to profound changes in various aspects of society. These limitations can influence demographics, economic growth, and even cultural values. When prospective parents are faced with constraints, it creates a ripple effect that touches on family structure, educational opportunities, and workforce dynamics.
One significant effect is often seen in the aging population. As birth rates decline, societies may face challenges in maintaining a balanced age distribution. This can result in a shrinking working-age populace, raising concerns about supporting the elderly. An increasing dependency ratio can strain public resources and healthcare systems.
Economically, restrictions can lead to a shortage of labor, affecting productivity and innovation. With fewer young individuals entering the workforce, industries may struggle to fill positions, potentially slowing economic growth. Moreover, consumer markets could experience shifts, as smaller family units may demand different products and services compared to larger families.
On a cultural level, social norms and values may evolve. Families with fewer children might prioritize different activities or lifestyles, which can influence educational systems and community planning. The perception of family and societal roles could undergo transformation as well, leading to new standards and expectations regarding parenting.
In essence, regulating the number of offspring can shape the very foundation of a society, affecting economic stability, demographic trends, and cultural identity. The wide-ranging implications warrant careful consideration and open dialogue among policymakers and communities alike.